Steel - Products
Hot rolled products consist of hot rolled coils and hot rolled steel sheets. Slabs produced from a continuous casting system are rolled, cooled and coiled into the sizes required by the customers.
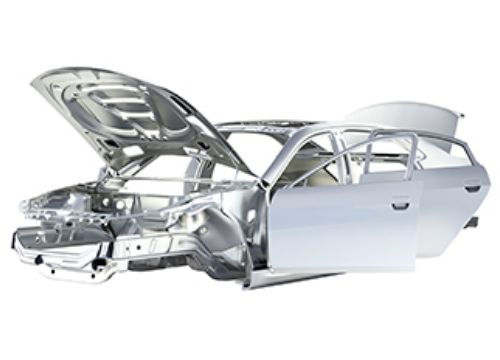
With six plants producing hot rolled steel and one high-mill plant in Pohang and Gwangyang, we manufacture 9.8 million tons of hot rolled steel products per year, securing global competitiveness. Hot rolled products are used extensively for various applications, including machines, architectural structures, car structures, general/API steel pipes, and cold rolling.
With six plants producing hot rolled steel and one high-mill plant in Pohang and Gwangyang, we manufacture 9.8 million tons of hot rolled steel products per year, securing global competitiveness. Hot rolled products are used extensively for various applications, including machines, architectural structures, car structures, general/API steel pipes, and cold rolling.
Type and Use
Steel for Cold Rolled Steel
This product is typically utilized for cold rolling and among hot rolled products, it exhibits the lowest strength. Its versatile applications span from regular drawing to deep drawing processes. It is also used in a variety of cold rolled products, including CR, GI, EG, and color plates.

Type and Use
High Strength Steel
It is made by adding silicon, manganese, nickel, chromium, copper, and other elements to carbon steel containing 0.2 percent of carbon for higher performance. High Strength Steel can be classified into bake-hardening steel, solid-solution strengthening, and precipitation hardening steel. It also has many variants: BH (Bake-Hardenable) steel, HSLA (high strength low alloy), R (rephosphorized) steel, IF (Interstitial Free) HSS, and ATOS (AuTOmobile Structural) steel.
Related Industries

Type and Use
High Carbon Steel
It contains carbon of no less than 0.30 wt.% or carbon of no less than 0.15 wt.% and has an alloy element to allow for heat treatment. After final heat treatment, it has high strength and hardness. Its common uses include automotive parts and industrial machines.
Related Industries

Type and Use
Steel Plate for Structure
Our products for this application include those for general structures, welding structures, and architectural structures. Their common uses include iron structures, bridges, ships, and vehicles.
Related Industries

Type and Use
Steel for Pipe and Tube
This product can be categorized into steel for structures, steel for pipes and drawing steel tubes. The product is extensively used for architectural structures, pipe piles, gas pipes, and car structures.
Related Industries

Steel plates are hot rolled products that have a relatively significant thickness. Products having a thickness of over 4.5 mm are classified as steel plates, and those having a thickness of over 100 mm are called thick steel plates.
Slabs of steel plates made through continuous casting are tailored to the dimensions specified by the customer through rolling and cooling before being cut into their final sizes.
POSCO uses a computerized automatic control over its entire process to produce high-quality steel plates. This allows us to ensure accuracy as well as full customization to meet customer needs. Our steel plates are extensively used for members for welded structures. Their common applications include shipbuilding, construction and heavy machines, offshore structures and wind farms, pressure vessels (storage tanks), and line pipes (oil pipelines). Primarily, chemical composition, material, dimensions, shape, surface, and internal quality are required for the product, and depending on intended use, additional requirements, such as weldability, workability, heat resistance, and anti-corrosion, may be necessary.
Slabs of steel plates made through continuous casting are tailored to the dimensions specified by the customer through rolling and cooling before being cut into their final sizes.
POSCO uses a computerized automatic control over its entire process to produce high-quality steel plates. This allows us to ensure accuracy as well as full customization to meet customer needs. Our steel plates are extensively used for members for welded structures. Their common applications include shipbuilding, construction and heavy machines, offshore structures and wind farms, pressure vessels (storage tanks), and line pipes (oil pipelines). Primarily, chemical composition, material, dimensions, shape, surface, and internal quality are required for the product, and depending on intended use, additional requirements, such as weldability, workability, heat resistance, and anti-corrosion, may be necessary.
Type and Use
Steel Plate for Shipbuilding
Shipbuilding steel refers to steel commonly used for shipbuilding. In fact, shipbuilding is the area where steel plates are most extensively used. Shipbuilding steel requires a wide variety of features in terms of strength, dimension, surface, form, and impact toughness (represented as grade A to F) depending on its application. All of our steel plates, including regular steel and high tensile steel approved by classification societies of many countries as well as TMCP-manufactured high tensile steel that allows for highly efficient electro-gas arc welding, are used for shipbuilding.
Related Industries

Type and Use
Steel Plate for Structure
Structural steel is commonly used for ground structures, welded structures, bridges, industrial machines, and many other similar areas of application. Wide applications mean a wide range of specifications used. Good weldability is crucial as welding is always involved in the use of these products. Additionally, strength that matches the intended application and specifications is imperative. Typical methods applied to the production of this product include regular rolling and TMCP processes, but heat treatment is often used when a high tensile strength of over 60 kg is needed.
Related Industries

Wire rods are available in the form of coils. The cross-section of the rod ranges from 5.5 to 42 mm in diameter. The billets and blooms produced in the continuous casting machine are rolled into billets, which are then rolled to the dimensions required by the customers, followed by cooling, coiling, and an inspection process before being manufactured.
POSCO uses a state-of-the-art facility and technology to produce wire rods. We use a fully computer-controlled automated system for the entire process to deliver products of various dimensions. Wire rods are used for wide applications ranging from key automotive components and materials for construction and bridge building to the most basic materials across various industries.
POSCO uses a state-of-the-art facility and technology to produce wire rods. We use a fully computer-controlled automated system for the entire process to deliver products of various dimensions. Wire rods are used for wide applications ranging from key automotive components and materials for construction and bridge building to the most basic materials across various industries.
Type and Use
Tire Cord Steel
It is made by adding elements (Cr, Si, Mn, etc.) to 0.70-0.92 percent high carbon steel for improved strength. This material is drawn into fine wires (0.15-0.38 mmø) that are subsequently twisted into tire cords (for use as reinforcement to protect tires from external pressure and shock for extended life).
Wire rods for tire cords require sufficient cleanness for drawing and lightness, and high strength for high fuel efficiency. Instead of pickling, more and more customers require mechanical descaling, and products that do not require heat treatment due to environmental concerns.
Wire rods for tire cords require sufficient cleanness for drawing and lightness, and high strength for high fuel efficiency. Instead of pickling, more and more customers require mechanical descaling, and products that do not require heat treatment due to environmental concerns.
Related Industries

Type and Use
Steel for CHQ
CHQ (cold heading quality) wire rods are used to make various mechanical parts, including bolts, nuts and screws, through forging and cold heading processes in both hot or cold state. Major applications include couplings for vehicles, bolts used in construction, and forged parts for mechanical equipment that require uniform chemical elements and good internal quality.
Related Industries

Cold rolled steel is made using hot rolled steel through pickling, cold rolling, and heat treatment. It is relatively thin with a thickness of 0.2 mm to 2.0 mm.
Cold rolled steel is highly aesthetic and easily machinable. Therefore, it is widely used as a premium steel product and an essential material in modern society.
We are striving to offer value-added products to our customers as demand for highly functional, cold rolled products is rising.
We operate two plants in Pohang and four in Gwangyang to produce cold rolled steel. Cold rolled steel’s applications range from home appliances, including vehicles, washing machines, and fridges, to industrial machinery and architectural materials. In addition, as new demands for the product emerge, including steel cans and steel houses, we focus on expanding the development and production fields of high-value-added products.
Cold rolled steel is highly aesthetic and easily machinable. Therefore, it is widely used as a premium steel product and an essential material in modern society.
We are striving to offer value-added products to our customers as demand for highly functional, cold rolled products is rising.
We operate two plants in Pohang and four in Gwangyang to produce cold rolled steel. Cold rolled steel’s applications range from home appliances, including vehicles, washing machines, and fridges, to industrial machinery and architectural materials. In addition, as new demands for the product emerge, including steel cans and steel houses, we focus on expanding the development and production fields of high-value-added products.
Type and Use
High Strength Steel
Featuring deep drawing and high strength, high strength steel can be classified into bake-hardening steel, solid-solution strengthening and precipitation hardening steel. It also has many variants, including BH (bake-hardenable) steel, HSLA (high strength low alloy), R (rephosphorized) steel, IF (interstitial free) HSS, ATOS (AuTOmobile structural) steel and HB (Hyper Burring) steel.
Related Industries
Type and Use
Black Plate for Tin Plating (BP)
Black plate (BP) refers to the raw plate material typically used for tin and chrome plating. After plating, customers use our black plates to make diverse containers such as cans for food and powdered milk, industrial tubes, 2-piece cans, tuna cans, easy open ends (EOEs), and butane gas cans.
Related Industries

Galvanized steel products are made by cleansing and heat-treating rolled coils before dipping them into a bath of molten zinc.
Through this process, the coils are plated with zinc only (GI), zinc and iron (GA), or zinc-aluminum-magnesium (PosMAC).
We deliver a wide range of galvanized steel products according to customer needs in terms of the type of plating, quantity, lubrication treatment, and post-treatment types. With good resistance to corrosion, formability, weldability, paintability, and other useful features, galvanized steel is finding expanded applications across various areas, including civil engineering, architecture, and automotive.
Through this process, the coils are plated with zinc only (GI), zinc and iron (GA), or zinc-aluminum-magnesium (PosMAC).
We deliver a wide range of galvanized steel products according to customer needs in terms of the type of plating, quantity, lubrication treatment, and post-treatment types. With good resistance to corrosion, formability, weldability, paintability, and other useful features, galvanized steel is finding expanded applications across various areas, including civil engineering, architecture, and automotive.
Type and Use
GI/GI(H)
GI takes place on the surface of a cold rolled plate, and GI(H) is applied to the surface of a hot rolled plate. During the solidification of molten zinc, the growth of zinc crystals is inhibited, resulting in the formation of fine crystalline grains. Its good plating reliability, rust inhibition, and cost-effectiveness make it an ideal product for various industries.
Related Industries

Type and Use
GA/GA(H)
GA is applied to the surface of cold rolled steel while GA(H) is applied to the surface of hot rolled steel. The base plate and zinc start to diffuse when heat is applied to form an alloyed plating layer. The product contains 9 to 13 percent iron, and it boasts excellent weldability, making it a popular material for automotive components.
Related Industries

Type and Use
PosMAC
PosMAC stands for POSCO Magnesium Aluminum alloy Coating Product, a high corrosion-resistant alloy-plated steel plate developed using POSCO's proprietary technology, comprising a ternary alloy of zinc, magnesium, and aluminum. PosMAC is a corrosion-resistant product that offers five to ten times superior corrosion resistance compared to normal hot-dip galvanized steel plates (GI, GI(H)) with the same amount of plating applied. It also demonstrates excellent corrosion resistance on every surface. Additionally, it boasts exceptional chemical and rust resistance, along with resistance to acids and alkalis. Its high hardness plating layer ensures excellent anti-galling performance and workability, enhanced by an outstanding friction coefficient. The product is utilized in applications where high corrosion resistance performance is required, such as photovoltaic support frames, buildings’ inner and outer walls, outdoor air conditioners units, and automotive components.
Related Industries

Electrogalvanized products are zinc-plated steel produced through an electrochemical process. The types of plating include Zn (zinc) and Zn-Ni (zinc-nickel) alloy plating.
POSCO's electrical galvanized steel features a beautiful surface finish and precise control over the amount of plating applied. This allows the steel to go through various post-treatments according to customer needs, including anti-fingerprint treatment and phosphate treatment. With good paintability, resistance to corrosion, weldability, and workability, it is extensively used in automotive and home appliances.
POSCO's electrical galvanized steel features a beautiful surface finish and precise control over the amount of plating applied. This allows the steel to go through various post-treatments according to customer needs, including anti-fingerprint treatment and phosphate treatment. With good paintability, resistance to corrosion, weldability, and workability, it is extensively used in automotive and home appliances.
Type and Use
Zn Electrical Galvanized Steel
This product is produced by electrochemically applying galvanizing to cold rolled steel surfaces. It offers various post-treatment choices, such as non-treatment, phosphate, and anti-fingerprinting. It is used for home appliances, automotive outer panels, and construction materials.
Related Industries

Type and Use
Anti-fingerprint Steel
This product is post-treated to prevent contamination by fingerprints during processing and use. With excellent functionality, corrosion resistance, paintability, and workability, it finds extensive use in video devices, OA devices, audio devices, computers, etc.
Related Industries

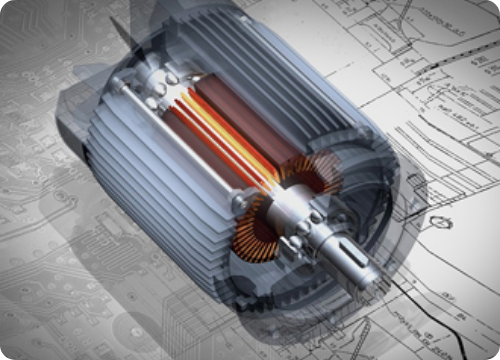
Electrical steel contains silicon to impart electromagnetic properties and is classified into grain-oriented (GO) and non-grain-oriented (NO) based on the rolling and magnetic characteristics' direction. Grain-oriented electrical steel (GO) has its internal crystals aligned in the rolling direction, significantly enhancing magnetic performance, and is primarily used in stationary products, such as transformers. Non-oriented electrical steel (NO) has uniformly distributed crystal directions in all directions and is used in rotating machinery, such as motors and generators. Recently, there has been a surge in demand for Hyper NO, a highly efficient, non-oriented electrical steel that minimizes energy losses in motors for electric vehicles and premium home appliances.
Type and Use
Grain Oriented Electrical Steel
Grain Oriented Electrical Steel (GO) is a product made with the direction of crystal magnetization aligned parallel to the rolling direction. This results in the product's superior magnetic properties. Based on the guaranteed iron loss standard, it is classified into Hyper GO and High GO, where products with an iron loss value of 0.85W/kg or less are called Hyper GO, and those with 1.05W/kg or less are referred to as High GO. It is used in large transformers, medium and small transformers, distribution transformers, and reactors.

Type and Use
Non Oriented Electrical Steel
Non Oriented Electrical Steel (NO) is an electrical steel that demonstrates uniform magnetic properties in the rolling direction and other directions. Based on the guaranteed iron loss standard, it is classified into Hyper NO and High NO, where products with an iron loss value of 3.5W/kg or less are called Hyper NO, and those with 6.0W/kg or less are referred to as High NO. It has an extensive range of applications ranging from large generators to small precision motors, rotating machinery cores, and small transformer cores.
Related Industries
Stainless steel is a special steel featuring a splendid surface and good resistance to rust. As a high-value-added product, stainless steel can be used for diverse areas without requiring any additional treatment.
POSCO operates an integrated production system that ranges from steel making to hot rolling and cold rolling, producing two million tons of stainless steel products every year. Stainless steel products can be classified into austenitic stainless steel, ferritic stainless steel, and martensitic stainless steel according to their alloy components and structural characteristics. Their typical applications include car exhaust pipes, kitchen appliances, electronics, and construction materials. Recently, their applications have expanded to electric vehicle battery cases and LNG storage tanks, garnering significant attention.
POSCO operates an integrated production system that ranges from steel making to hot rolling and cold rolling, producing two million tons of stainless steel products every year. Stainless steel products can be classified into austenitic stainless steel, ferritic stainless steel, and martensitic stainless steel according to their alloy components and structural characteristics. Their typical applications include car exhaust pipes, kitchen appliances, electronics, and construction materials. Recently, their applications have expanded to electric vehicle battery cases and LNG storage tanks, garnering significant attention.
Type and Use
Austenitic Series (300 Series)
Among stainless steels, the most widely used type is the austenitic-type stainless still. This product includes chromium and nickel components, which provide excellent formability, weldability, and corrosion resistance. The representative austenitic stainless steel is 304 steel, and by adding alloying elements such as Mo, Ti, Cu, specialized grades suitable for specific purposes, such as 316L, 321, and 304J1, have been developed. Common applications include kitchen appliances, construction materials, and chemical equipment.
Related Industries

Type and Use
Ferritic Series (400 Series)
Ferritic stainless steels, with chromium as the main alloying element, have a low thermal expansion coefficient and excellent corrosion resistance. The representative ferritic stainless steel is 430, and by adding alloying elements such as Ti, Nb, Mo, specialized grades for specific purposes, such as 409L, 430J1L, and 444, have been developed. Common applications include exhaust systems and home appliances.
Related Industries
